Full Spectrum Efficacy
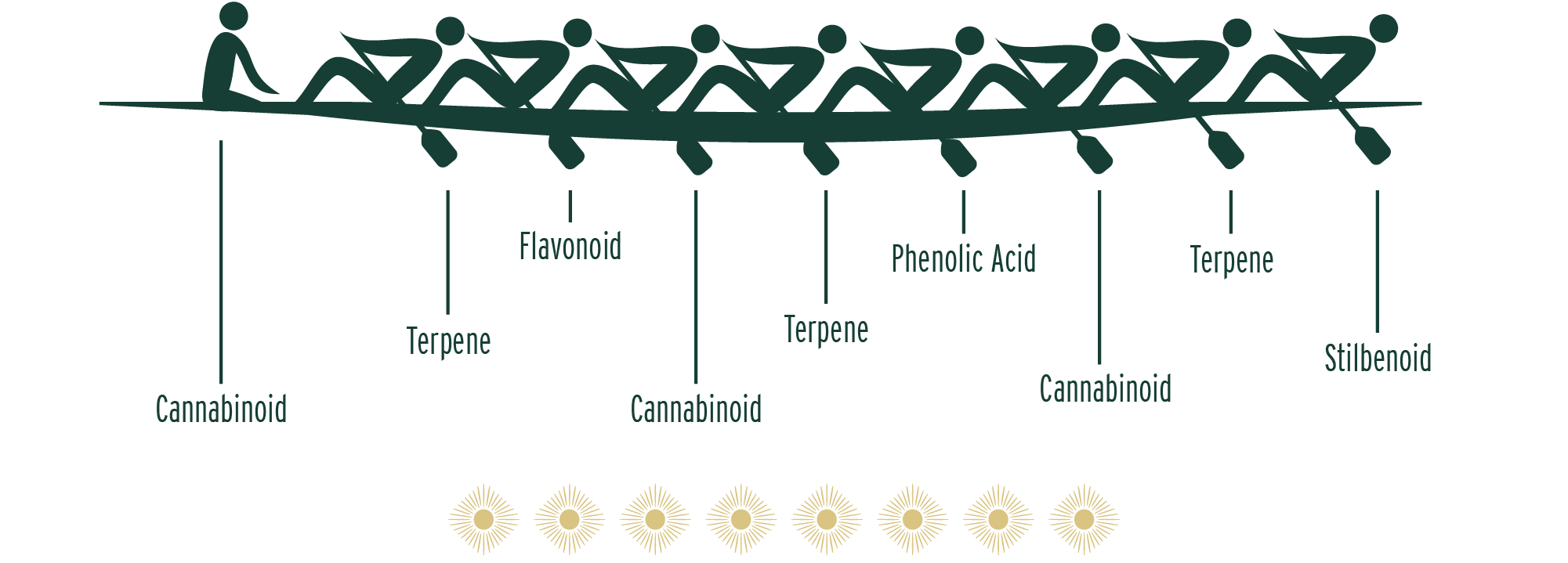
Cannabis is a phytochemical powerhouse, containing 120+ cannabinoids, 400+ terpenes, 20+ flavonoids, and an unknown number of phenolic acids and stilbenoids. All of these classes of phytochemicals demonstrate beneficial activity — anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antioxidant, and much more. Research shows that the safest and most effective cannabis products are those containing the full spectrum of phytochemicals working together as nature intended. Alcohol is the only common solvent that extracts all these components, which is why we extract our RSO exclusively with certified organic cane alcohol. Siskiyou Sungrown RSO has always contained the True Full Spectrum of beneficial phytochemicals, for maximum safety and efficacy.
Broad Spectrum
Broad Spectrum products are extracted with CO2, hydrocarbons like butane, and other common solvents. They typically contain cannabinoids and terpenes, but not flavonoids, phenolic acids, stilbenoids, and other powerful therapeutic compounds. Broad Spectrum products are great for vaping or dabbing, but not as effective for therapeutic use.
Distillate
Distillates typically contain only cannabinoids, limiting the therapeutic benefit.
Isolate
Isolates contain just a single cannabinoid. They have the fewest therapeutic benefits, and research demonstrates a higher potential for unwanted side effects.
Full Spectrum Definitions
-
Cannabinoids:
There are over 120 cannabinoids produced by the cannabis plant that have been identified thus far. These include CBD (cannabidiol), THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), CBG (cannabigerol), CBC (cannabichromene), and CBN (cannabinol). Phytocannabinoids, as well as endocannabinoids (produced by our body), interact with our body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS) and other chemical receptor pathways to regulate fundamental physiological and cognitive functions. The goal of the ECS is to produce homeostasis, or equilibrium, within the organism. Cannabinoids fit like keys in receptor cells, causing the release of specific chemicals which act on the body’s systems to produce balance.
-
Terpenes:
Terpenes are the essential oil phytochemicals responsible for a plant’s aroma and flavor. There are over 400 terpenes produced by cannabis, including limonene, myrcene, and linalool. Terpenes engage biochemical receptors throughout the body, including the ECS, generating an array of beneficial pharmacological activity. Extensive research has identified many healthful properties of terpenes, including anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anxiolytic, anticancer, anticonvulsant, anti-bacterial, and anti-fungal.
-
Polyphenols:
Polyphenols are a class of phytochemicals that includes flavonoids, phenolic acids, and stilbenoids. Cannabis produces over 20 flavonoids, including at least three which are unique to this plant. Two of them, cannaflavins A and B, have been shown to provide 30 times the anti-inflammatory benefit of aspirin. According to published research, “there is a correlation between dietary phenolic compound intake and a reduced incidence of chronic diseases such as cancers, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.” This beneficial activity is thought to be in part the result of the amplification of antioxidant activity by phenolic compounds.